

The number of protons determines the element, but the number of neutrons in the atom of any one element can vary.
#FUN FACTS ABOUT CAESIUM PLUS#
The mass number represents the number of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of the element. The number written to the right of the element's name is the mass number. Isotopes differ from each other according to their mass number. Isotopes are two or more forms of an element.
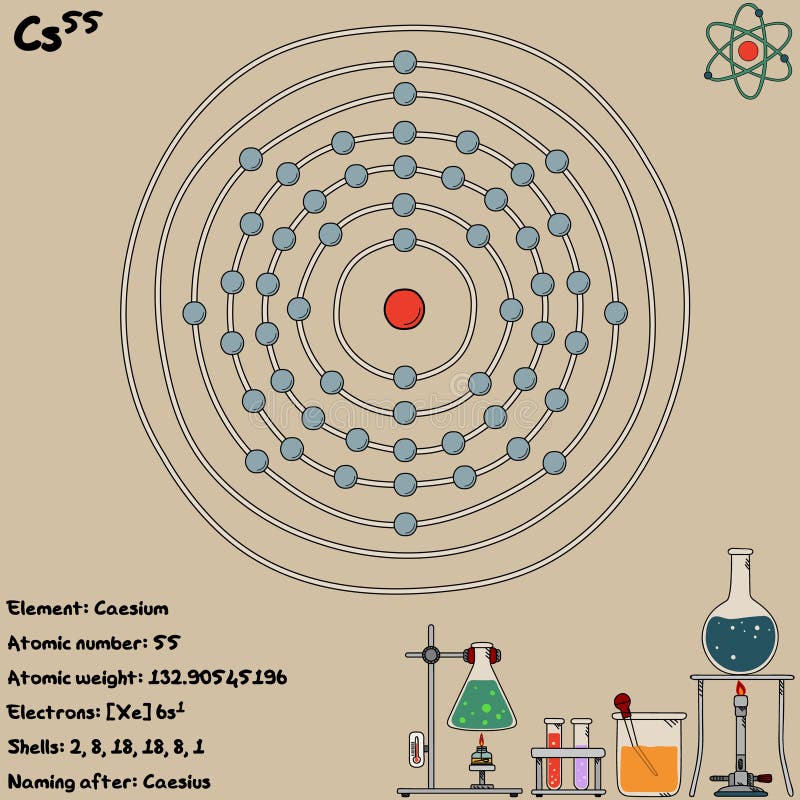
Only one naturally occurring isotope of cesium is known, cesium-133. Cesium is also found in small amounts in a mineral of boron called rhodizite. This ore is mined in large quantities at Bernic Lake, in the Canadian province of Manitoba.

The mineral containing the largest fraction of cesium is pollucite (Cs 4Al 4Si 9O 26). It is often found in an ore of lithium called lepidolite. Of the chemical elements in terms of their abundance in the earth.Ĭesium occurs in small quantities in a number of minerals. The abundance of cesium in the Earth's crust has been estimated at about 1 to 3 parts per million. Cesium must be stored under kerosene or a mineral oil to protect it from reacting with oxygen and water vapor in the air.Ĭesium also reacts vigorously with acids, the halogens, sulfur, and phosphorus. Hydrogen gas ignites immediately as a result of the heat given off by the reaction. In the reaction with water, hydrogen gas is released. It combines quickly with oxygen in the air and reacts violently with water. Chemical propertiesĬesium is a very reactive metal. It melts easily in the heat of one's hand, but should never be handled that way! Cesium's boiling point is 705 ☌ (1,300 ☏), and its density is 1.90 grams per cubic centimeter. Ductile means capable of being drawn into thin wires. Physical propertiesĬesium is a silvery-white, shiny metal that is very soft and ductile. Bunsen suggested calling the element cesium, from the Latin word caesius for "sky blue." For many years, the name was also spelled caesium. These elements were already well known.Īfter Bunsen and Kirchhoff removed all these elements from their sample, they were surprised to find two beautiful blue lines in the spectrum of the "empty" spring water. They saw spectral lines for sodium, potassium, lithium, calcium, and strontium. In 1859, Bunsen and Kirchhoff were studying a sample of mineral water taken from a spring. Such was the case with the discovery of cesium. Using spectroscopy, a chemist can identify the elements by these distinctive lines. When the substance is heated, the hidden elements give off characteristic spectral lines. But the element is much easier to detect by spectroscopy.

In many cases, the amount of an element present in a sample is too small to see. The invention of spectroscopy gave chemists a powerful new tool. One of its radioactive isotopes, cesium-137, is widely used in a variety of medical and industrial applications.
#FUN FACTS ABOUT CAESIUM SERIES#
The spectrum (plural: spectra) of an element consists of a series of colored lines.Ĭesium is not a common element, and it has few commercial uses. The light produced is different for every element. Spectroscopy is the process of analyzing light produced when an element is heated. They found the element using a method of analysis they had just invented: spectroscopy. Although in theory francium is more active than cesium, francium is too rare to have any commercial uses.Ĭesium was discovered in 1861 by German chemists Robert Bunsen (1811-99) and Gustav Kirchhoff (1824-87). Cesium is considered the most active metal. The alkalis include lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, and francium. The periodic table is a chart that shows how chemical elements are related to each other. OverviewĬesium is a member of the alkali family, which consists of elements in Group 1 (IA) of the periodic table. Note: This article, originally published in 1998, was updated in 2006 for the eBook edition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
